Tumor Cytobiology of IGF-1R in Breast Tumor Activation and Propagation; And the Role of Celecoxib in its Inhibition
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.23958/mcha/vol02/i10/40Keywords:
Breast Cancer Subtypes, Celecoxib, Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Receptor (IGF-1R) Inhibition, Metastasis, Angiogenesis.Abstract
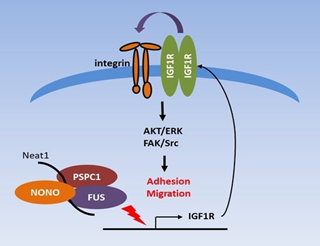
The Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Receptor (IGF-1R) stands as a central orchestrator in cellular signaling, governing pivotal processes encompassing growth, proliferation, and differentiation. Its aberrant activation is intricately intertwined with the pathogenesis and progression of breast cancer, a heterogeneous disease presenting formidable clinical challenges. Amidst the burgeoning landscape of therapeutic interventions, Celecoxib, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), has emerged as a promising candidate for targeting the dysregulated IGF-1R pathway. This review delineates the intricate molecular mechanisms underlying Celecoxib's modulation of the IGF-1R pathway, elucidating its pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic implications in breast cancer management. Celecoxib exerts inhibitory effects on IGF-1R through multifaceted molecular interactions, impeding receptor activation and downstream signaling cascades pivotal for tumor proliferation and metastasis. Furthermore, it regulates IGF-1R expression at both transcriptional and translational levels, exerting nuanced control over cellular responses. Moreover, Celecoxib's therapeutic impact transcends mere IGF-1R inhibition, as it potentiates pro-apoptotic pathways and disrupts tumor-permissive microenvironments. A nuanced understanding of Celecoxib's pharmacokinetic profile is imperative, considering its sustained and targeted inhibition of IGF-1R signaling, and its potential synergistic effects in combinatorial therapeutic regimens for breast cancer. This comprehensive elucidation underscores the paramount importance of deciphering Celecoxib's intricate molecular interplay with the IGF-1R pathway, heralding novel avenues for precision medicine and tailored therapeutic interventions in the management of breast cancer.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Maher Monir. Akl, Amr Ahmed (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Creative Commons License All articles published in Medicine & Community Health Archives are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.



